Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (SVC)
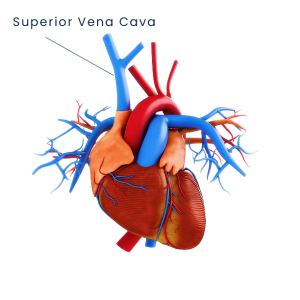
What is the Superior Vena Cava?
The superior vena cava is a major vein in your upper body that carries blood from your head, neck, upper chest, and arms to the heart.
What is Superior Vena Cava Syndrome?
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome (commonly referred to as SVC or SVCS) is a condition where the blood flow through the superior vena cava is restricted or slowed down. This slowed blood flow may be caused by a blood clot, tumor, or other nearby tissue compressing the vein.
What are the risk factors for Superior vena cava syndrome?
- Smoking
- History of smoking
- Localized edema of face or upper extremities
- Central venous access ports
- Multiple pacemaker leads
- Over 50 years of age
What are the Signs & Symptoms of Superior Vena Cava Syndrome?
- Swelling in face, neck, or upper body
- Trouble breathing or shortness of breath
- Coughing
- Pale or blue skin in the face
- Swollen veins in chest, neck or arms
- Chest pain
- Hoarse voice, difficulty speaking, or trouble swallowing